Our most recently completed studies
- Dietary Sodium Intervention to Reduce Tissue Sodium in Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Hemodialysis Patients (DSMRI)
- Working on Wellness
- Cardiac Output and Central-Venous Oxygen Saturation in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients
- Hemodialysis Lifestyle Intervention Trial
- Observational study on hydration status of maintenance hemodialysis patients
- Sodium magnetic resonance imaging (NaMRI) assessment of tissue sodium stores in hemodialysis patients
- Positive Psychology Intervention to Reduce Depressive Symptoms in Hemodialysis Patients (Upgrowth)
- Validation of commercially available activity trackers in hemodialysis patients (AT)
- Gut microbiota-mediated effects of inulin supplementation on mineral metabolism in maintenance hemodialysis patients (HIT-MBD)
- Cross-sectional analysis of gut microbiome and clinical risk factors in maintenance hemodialysis patients (COSMIC)
- Acute effects of exercise on cardiovascular response during dialysis (ACE-HD)
- IntraHemodialytic Oral Protein and Exercise (IHOPE)
- Acute effects of nutrition supplementation on treatment efficiency and hemodynamics during dialysis (Nepro)
Effects of Pomegranate Supplementation on Physical Function and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
 The POM pilot study aimed to evaluate the effects of pomegranate extract supplementation on cardiovascular disease risk, physical function, body composition, and quality of life in patients with end-stage renal failure on maintenance hemodialysis.
The POM pilot study aimed to evaluate the effects of pomegranate extract supplementation on cardiovascular disease risk, physical function, body composition, and quality of life in patients with end-stage renal failure on maintenance hemodialysis.
Excessive oxidative stress and inflammation is believed to underlie many of the cardiovascular complications in patients with chronic kidney disease. This suggests that antioxidant therapy, such as that from pomegranate, could be efficacious to attenuate these complications.
Learn more about the POM study on ClinicalTrials.gov
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Exercise Training in Hemodialysis Patients
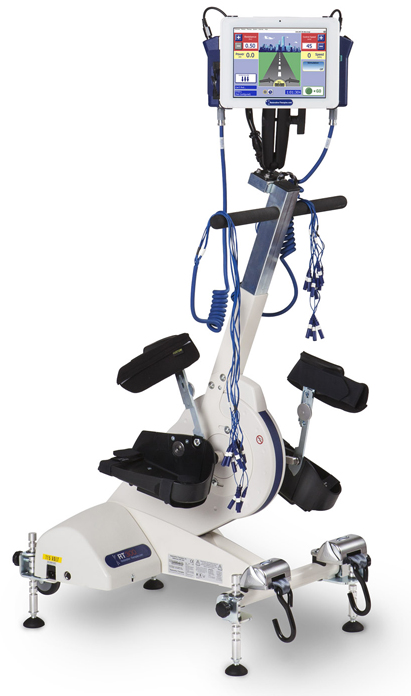 Functional electrical stimulation (FES)-enhanced cycling is a new form of exercise using a motor-assisted cycle coupled with electrical stimulation that stimulates leg muscles to pedal. FES exercise has been shown to be beneficial and has been safely used as an activity based rehabilitation therapy in patients with severe disabilities such as spinal cord injury or stroke patients.
Functional electrical stimulation (FES)-enhanced cycling is a new form of exercise using a motor-assisted cycle coupled with electrical stimulation that stimulates leg muscles to pedal. FES exercise has been shown to be beneficial and has been safely used as an activity based rehabilitation therapy in patients with severe disabilities such as spinal cord injury or stroke patients.
A few pilot studies have also demonstrated that FES therapy has the potential to improve function in other disabled populations, including chronic heart failure and stroke patients. However, its effects in other populations with significant physical impairments, including CKD patients, have yet to be established.
The objective of FES study is to evaluate the effects of FES-cycling training on measures related to physical function, heart disease, bone health and QOL in dialysis patients with relatively low levels of physical function.
Learn more information of our FES project on ClinicalTrials.gov
Kaatsu Training

Kaatsu training, also called blood flow restricted exercise or occlusion training, is as an alternative, lower-intensity exercise method. This type of exercise is done by inflating a cuff around the exercising limb, partially restricting blood flow to the muscle.
Kaatsu has been shown to result in gains in muscle size and strength similar to high load training, however, Kaatsu is done at intensities of 20-40 percent of an individual’s one-repetition maximum. Therefore, it may be an effective form of exercise in populations that cannot exercise at high intensities.
We have done two Kaatsu training studies. We hope to determine participants’ response to Kaatsu training and try to determine a way by which Kaatsu can be performed, and still be effective with less discomfort to the participants.
Kaatsu resistance training, muscle strength and physical function in persons with multiple sclerosis
Purpose: To determine the effects of Kaatsu strength training on lean mass, strength, balance, and quality of life in multiple sclerosis patients.
Kaatsu resistance training, muscle strength and inflammation in chronic kidney disease patients
Purpose: To determine the effects of Kaatsu cycling on lean mass, strength, physical function and cardiovascular disease risk in stage 2 – 4 chronic kidney disease patients.
Efficacy of Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate (HMB) Supplementation in Hemodialysis Patients
Beta-hydroxy beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) represents a potential low-cost nutritional intervention to attenuate muscle loss in hemodialysis patients. HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine that has been shown to safely increase muscle mass in other clinical populations with prevalent muscle loss, such as the elderly, cancer, and AIDS patients primarily through reductions in skeletal muscle protein catabolism.
The purpose of the trial is to determine if oral supplementation with HMB attenuates muscle loss, improves muscle strength, physical function, fall risk and quality of life in hemodialysis patients.
Learn more about our HMB project on ClinicalTrials.gov

